Multilingual Application: Implementing Localization with BLoC in Flutter
— 9 min read
Flutter enthusiasts, get ready to take your app development prowess to the next level! Are you seeking to elevate your Flutter applications with seamless multilingual support and efficient state management? Look no further. Embark on a seamless journey through the intricate world of Flutter localization, enriched with the power of BLoC for efficient state management. In this comprehensive guide, we'll demystify the process, empowering you to effortlessly create dynamic, user-friendly applications that adapt effortlessly to your audience's location and language preferences.
In case you are wondering what localization is all about, allow me to give you a quick explanatoin.Localization in an application is the process of tailoring the app's content, user interface, and functionality to cater to the unique language, cultural, and regional preferences of its users. Not only does it involve tasks like translating text, adapting date and time formats, and using region-specific currency symbols, but it also empowers developers to create custom text in multiple languages. This means you can provide users with a personalized, native experience by offering content and messages in their preferred language. Localization is the key to breaking down language and cultural barriers, ensuring that your app is accessible and user-friendly to a diverse, global audience.
Now that we've covered the basics, it's time to roll up our sleeves and dive into the nitty-gritty. Grab your coding gear and get ready to become the Mr. Worldwide of the Flutter world. Dale!

Setting up Localization
Step 1: Installing Required Packages
The initial step in setting up Flutter localization is installing the required packages. Open your terminal and run the following commands:
flutter pub add flutter_localizations --sdk=flutter
flutter pub add intl:any
By running those two commands, you install all the necessary dependencies to your project. This is what you should see on your pubspec.yaml file :
dependencies:
flutter:
sdk: flutter
flutter_localizations:
sdk: flutter
intl: any
As you begin to witness the initial changes taking place in your app, it's time to configure the supported languages. Flutter provides a comprehensive list of supported languages that you can integrate into your application. You can check all the available languages here. Utilize the following code snippet to set up the language configuration within your MaterialApp:
// import the package so you can benefit from it
import 'package:flutter_localizations/flutter_localizations.dart';
MaterialApp(
title: 'Multilanguage Flutter App with BLoC',
localizationsDelegates: [
GlobalMaterialLocalizations.delegate,
GlobalWidgetsLocalizations.delegate,
GlobalCupertinoLocalizations.delegate,
],
supportedLocales: [
Locale('en'), // English
Locale('el'), // Greek
],
home: HomePage(),
),
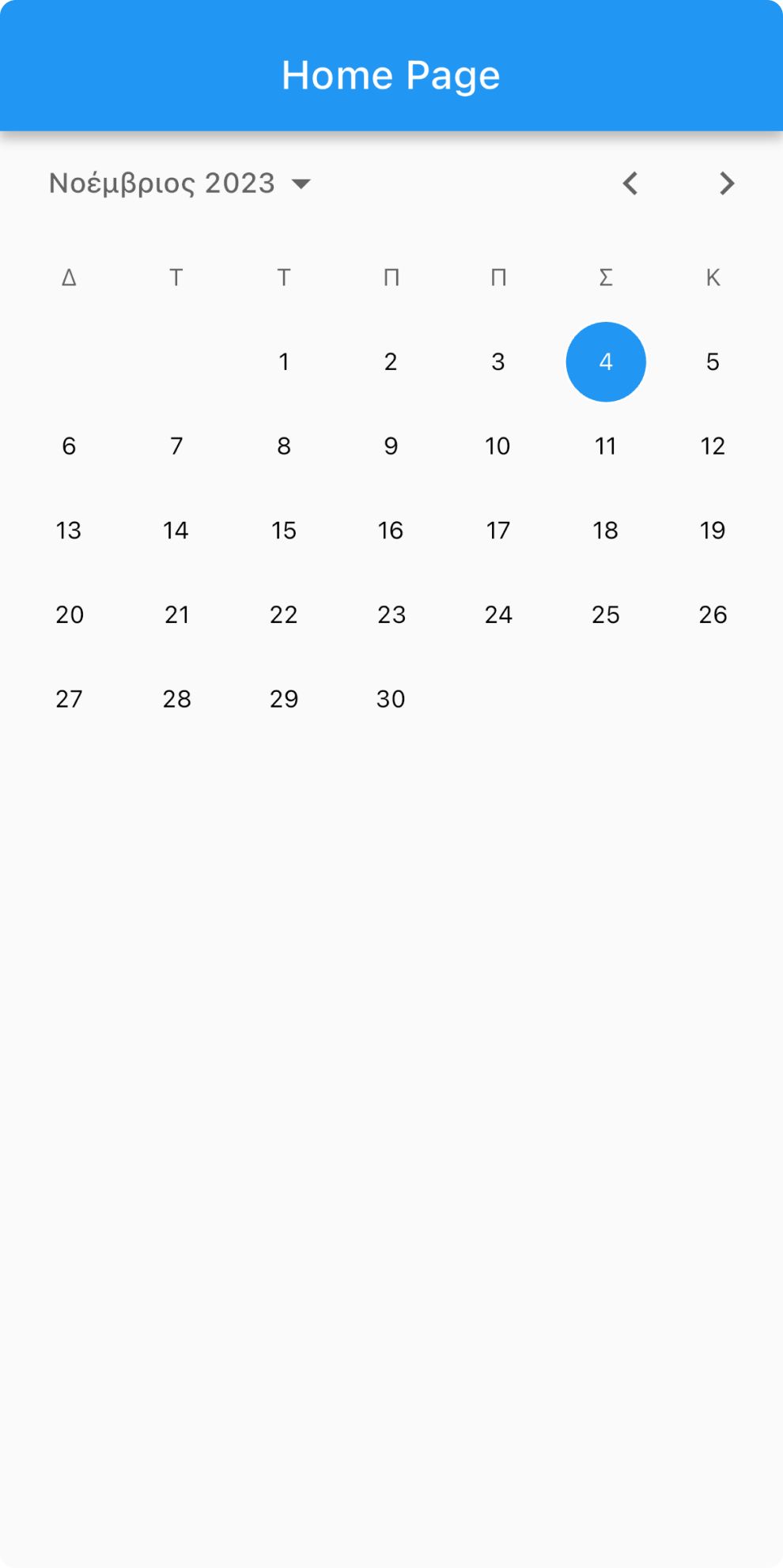
Furthermore, let's explore a quick example of how localization works within a calendar. Consider integrating the following code snippet into your application:
class HomePage extends StatelessWidget {
const HomePage({Key? key});
@override
Widget build(BuildContext context) {
return Scaffold(
appBar: AppBar(
title: const Text('Home Page'),
),
body: Builder(
builder: (context) {
return CalendarDatePicker(
initialDate: DateTime.now(),
firstDate: DateTime(1900),
lastDate: DateTime(2100),
onDateChanged: (value) {},
);
},
),
);
}
}
With this example, you can visualize how localization can be implemented within a specific widget, such as the calendar, to reflect the preferred language and regional settings of your users.
Step 2: Setup your own text
Now that the basic localization setup is in place, let's take customization to the next level by incorporating your own text. This step allows you to tailor the app's content based on your specific needs, providing a personalized touch to your Flutter application.
Open your pubspec.yaml file and enable the code generation flag. This flag is situated in the flutter section of the pubspec.yaml file:
flutter:
generate: true # Add this line
Next, add a new yaml file to the root directory of your Flutter project and name it l10n.yaml. Include the following content:
arb-dir: lib/l10n
template-arb-file: app_en.arb
output-localization-file: app_localizations.dart
Create a folder inside the lib folder with the name l10n (matching the name specified in the arb-dir section of l10n.yaml). Within this folder, create files for each language you've chosen. In this example, we'll create:
- app_en.arb
- app_el.arb
Inside these language files, define the variables for the text you want to use and assign values based on the language. Ensure that the variable names are consistent across different language files:
app_en.arb
{
"exampleText" : "Welcome"
}
app_el.arb
{
"exampleText" : "Καλώς ήρθες"
}
Now, to kickstart the generation of localizations and witness your personalized text in action, all you have to do is open your terminal and run one of the following commands:
flutter pub get
or
flutter run
You should find generated files in ${your_flutter_project_name} / .dart_tool / flutter_gen / gen_l10n.
.dart_tool
├── flutter_gen
│ ├── gen_l10n
│ │ ├── app_localizations.dart <--
│ │ ├── app_localizations_en.dart <--
│ │ └── app_localizations_id.dart <--
│ └── pubspec.yaml
Finally, it's time to make some adjustments in your MaterialApp. Open your main.dart file and modify your MaterialApp as follows:
const MaterialApp(
debugShowCheckedModeBanner: false,
title: 'Multilanguage Flutter App with BLoC',
locale: Locale('el'), // Set the locale you want the app to display messages
localizationsDelegates: [
AppLocalizations.delegate, // Add this line
GlobalMaterialLocalizations.delegate,
GlobalWidgetsLocalizations.delegate,
GlobalCupertinoLocalizations.delegate,
],
supportedLocales: [
Locale('en'), // English
Locale('el'), // Greek
// Add more supported locales based on your application's target audience
],
home: HomeScreen(),
),
In this modification, the locale property is set to 'el' (Greek) by default. Adjust this value to your preferred locale, or you can dynamically change it based on user preferences.
By adding AppLocalizations.delegate to the localizationsDelegates, you're ensuring that your custom localization logic is incorporated into the app, allowing it to seamlessly display your personalized text.
If you want to display your text, just add a Text widget in your application and set the String value with one of your texts inside your .arb files.
import 'package:flutter_gen/gen_l10n/app_localizations.dart'; // don't forget to import the package
...
Text(AppLocalizations.of(context)!.exampleText,),
...
With these adjustments, your MaterialApp is now equipped to provide a tailored multilingual experience. In the next steps, we'll integrate BLoC for efficient state management, bringing your Flutter app to a new level of dynamism.
Setting up Language Model
Create a language folder inside the lib folder. Next, create another folder and name it model. This is where we are going to create our language_model.dart file and place the code below :
import 'dart:ui';
enum Language {
english(
Locale('en', 'US'),
'English',
),
greek(
Locale('el', 'EL'),
'Ελληνικά',
);
const Language(
this.value,
this.text,
);
final Locale value;
final String text;
}
That's all for this part, now let's see how to use this language model and control the state of our application with it.
Setting up BLoC
Step 1: Installing BLoC Packages
Before we dive into the BLoC magic, ensure you have the necessary packages installed. Open your terminal and run the following commands:
flutter pub add flutter_bloc
flutter pub add bloc
flutter pub add equatable
Step 2: BLoC Files
Now, let's create the BLoC files that will orchestrate the language-related state changes. In your language folder, create the following three files within a language_bloc folder:
language_state.dart
part of 'language_bloc.dart';
class LanguageState extends Equatable {
const LanguageState({
Language? selectedLanguage,
}) : selectedLanguage = selectedLanguage ?? Language.greek;
final Language selectedLanguage;
@override
List<Object> get props => [selectedLanguage];
LanguageState copyWith({Language? selectedLanguage}) {
return LanguageState(
selectedLanguage: selectedLanguage ?? this.selectedLanguage,
);
}
}
language_event.dart
part of 'language_bloc.dart';
abstract class LanguageEvent extends Equatable {
const LanguageEvent();
@override
List<Object> get props => [];
}
class ChangeLanguage extends LanguageEvent {
final Language selectedLanguage;
const ChangeLanguage({
required this.selectedLanguage,
});
@override
List<Object> get props => [selectedLanguage];
}
language_bloc.dart
import 'package:bloc/bloc.dart';
import 'package:equatable/equatable.dart';
import '../model/language_model.dart';
part 'language_event.dart';
part 'language_state.dart';
class LanguageBloc extends Bloc<LanguageEvent, LanguageState> {
LanguageBloc() : super(const LanguageState()) {
on<ChangeLanguage>(onChangeLanguage);
}
onChangeLanguage(ChangeLanguage event, Emitter<LanguageState> emit) async {
emit(state.copyWith(selectedLanguage: event.selectedLanguage));
}
}
Step 3: Integrating BLoC in Your App
With your BLoC files ready, let's integrate BLoC into your Flutter app. Open your main.dart file and modify your app's structure as follows:
import 'package:flutter/material.dart';
import 'package:flutter_bloc/flutter_bloc.dart';
import 'package:flutter_localizations/flutter_localizations.dart';
import 'package:flutter_gen/gen_l10n/app_localizations.dart';
import 'home_screen.dart';
import 'language/language_bloc/language_bloc.dart';
void main() {
runApp(
BlocProvider<LanguageBloc>(
create: (context) {
return LanguageBloc();
},
child: const MyApp(),
),
);
}
class MyApp extends StatelessWidget {
const MyApp({super.key});
@override
Widget build(BuildContext context) {
return BlocBuilder<LanguageBloc, LanguageState>(
builder: (context, state) {
return MaterialApp(
debugShowCheckedModeBanner: false,
title: 'Multilanguage Flutter App with BLoC',
locale: state.selectedLanguage.value,
localizationsDelegates: const [
AppLocalizations.delegate,
GlobalMaterialLocalizations.delegate,
GlobalWidgetsLocalizations.delegate,
GlobalCupertinoLocalizations.delegate,
],
supportedLocales: const [
Locale('en'), // English
Locale('el'), // Greek
],
theme: ThemeData(
useMaterial3: true,
colorSchemeSeed: Colors.blue,
),
home: const HomeScreen(),
);
},
);
}
}
Bringing it All Together: Your Multilingual Flutter App
Congratulations! you've successfully learned how to use Flutter localization and the powerful state management features of BLoC. Now, let's see your newfound knowledge in action with a small project that includes everything we've learned.
Explore the Multilanguage Flutter App Project
Behold, a compact yet feature-packed project that showcases the seamless integration of localization and BLoC. Here's a sneak peek at what you can expect:
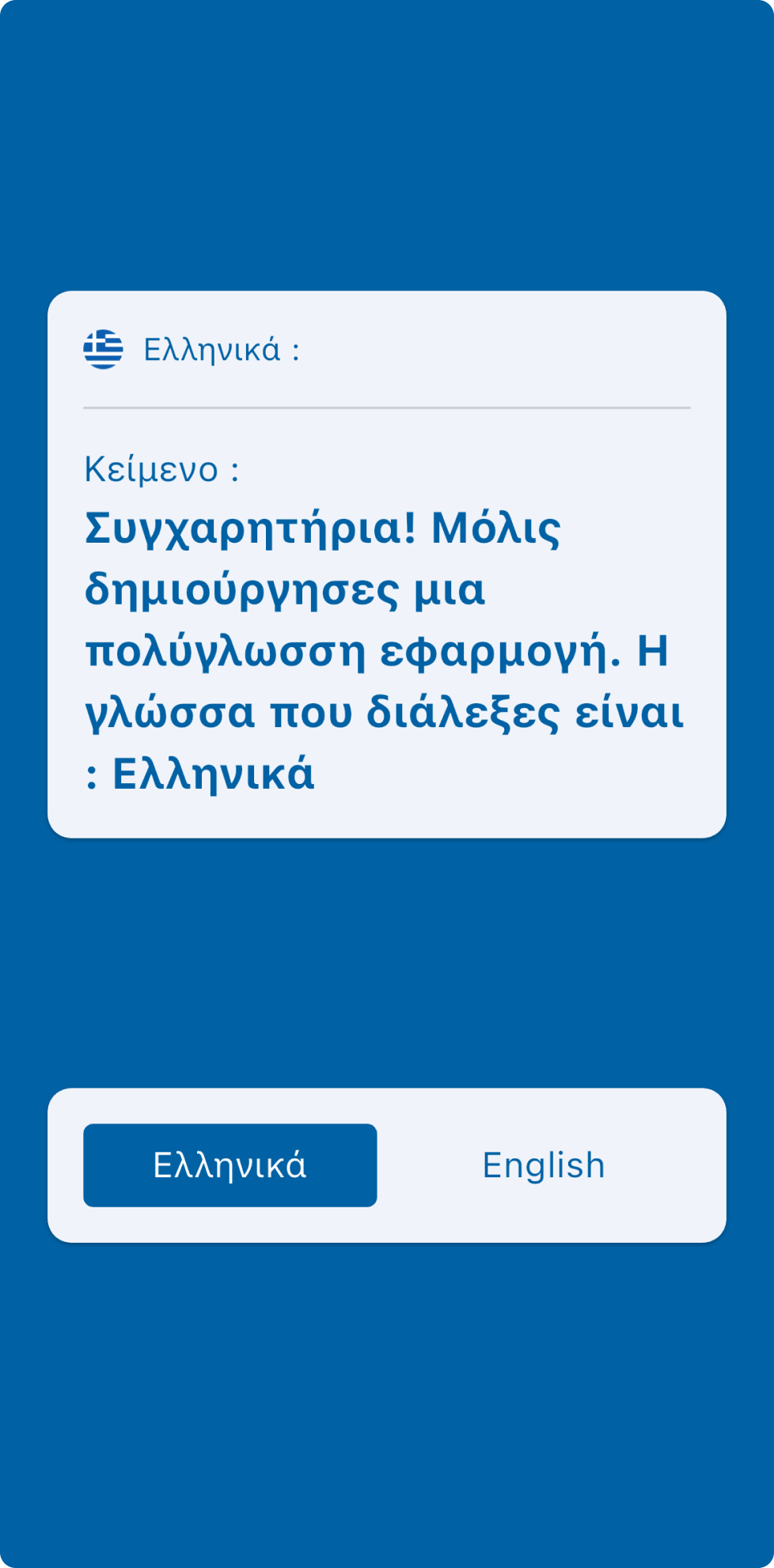
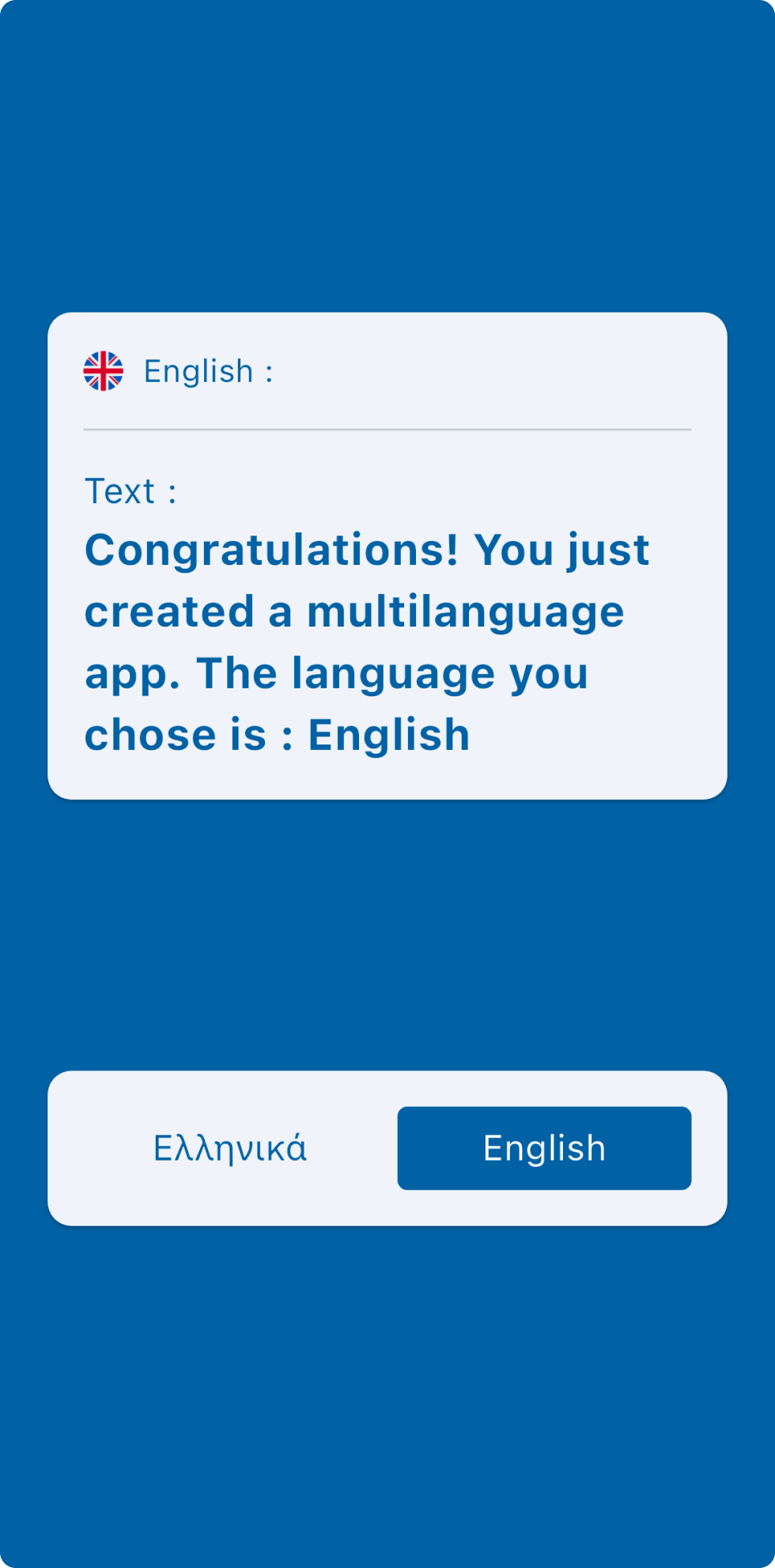
Dive Deeper: Explore the GitHub Repository
If you're eager to delve deeper into the implementation details, explore the complete project on GitHub. This repository provides a hands-on experience, allowing you to dissect the code, experiment with different configurations, and truly grasp the synergy between localization and BLoC.
With this project, you have a tangible resource to reinforce your understanding and elevate your Flutter app development skills. Feel free to customize, expand, and adapt the code to suit the unique requirements of your future projects.
And now...you deserve to call yourself the Mr.Worldwide of the Flutter World!🌎 Wishing you a fantastic day ahead, happy coding, and looking forward to catching up with you soon!
Was this guide helpful? Consider buying me a coffee!☕️ Your contribution goes a long way in fuelling future content and projects. Buy Me a Coffee.